Mean change in I-PSS scores was –2.2 with sildenafil and
–3.2 with alfuzosin or doxazosin (insufficient SOE)
[47,48]. Mean change in I-PSS scores with sildenafil
25 mg was 4.0 points versus 5.4 points for tamsulosin
0.4 mg (insufficient SOE)
[49].
Evidence was insufficient for overall withdrawals and
withdrawals due to AEs.
3.13.
Tadalafil AB combination versus AB monotherapy
Four trials (
n
= 224) compared tadalafil combined with an AB
versus AB monotherapy
[41,45,46,50]. Two 3-mo trials
compared tadalafil 10 mg daily
[45]or 20 mg on alternate
days
[46]combined with alfuzosin 10 mg to alfuzosin 10 mg
monotherapy. Two trials evaluated tadalafil combined with
tamsulosin 0.4 mg versus tamsulosin 0.4 mg monotherapy:
a 1-mo trial evaluated tadalafil 5 mg daily
[50]and a 4-mo
trial evaluated tadalafil 10 mg daily
[41]. Nearly all
participants had a history of ED
[41,45,46] .All trials were
open label except Regadas et al
[50]and the overall RoB
therefore ranged from moderate to high.
Results with combination therapy were similar to AB
monotherapy (tadalafil 5–20 mg combined with AB was no
different than AB monotherapy in improving mean I-PSS
scores from baseline [WMD: –2.0, 95% CI: –4.03 to –0.00;
insufficient SOE]). Mean reductions in I-PSS scores were
similar; 10.4 and 8.6 with combination and monotherapy.
Improvement in mean I-PSS QoL scores was also not
significantly different between combination treatment and
monotherapy; however, only open label (high RoB) trials
reported this outcome (low SOE)
[41,45,46]. Evidence was
insufficient for overall withdrawals and withdrawals due to
AEs.
3.14.
Sildenafil AB combination versus AB monotherapy
Four trials (
n
= 281) compared sildenafil combined with an
AB versus AB monotherapy
[47–49,51] .Two 3-mo trials
evaluated sildenafil combined with alfuzosin 10 mg versus
alfuzosinmonotherapy; one used daily sildenafil 25 mg
[48]and the other used sildenafil 50 mg (dosing frequency not
reported)
[51] .One 4-mo trial evaluated sildenafil 50 mg
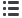
Table 7 – Evidence overview of tadalafil 10–20 mg versus alfuzosin 10 mg monotherapy
Outcome
No. of trials
(evaluated)
Intervention,
% (
n
/
N
) or mean
Control,
% (
n
/
N
) or mean
Results and magnitude
of effect (95% CI)
Strength
of evidence
Responders
Not reported
Insufficient
I-PSS score, mean change from baseline 2 (87)
Range
–1.3 to –6.3
Range
–5.2 to –9.5
Studies not pooled. Both favored alfuzosin.
Lo
w a , bI-PSS QoL, mean change from baseline 2 (87)
Range
–1.0 to –2.4
Range
–1.3 to –3.2
Studies not pooled. Both favored alfuzosin
Lo
w a , bOverall withdrawals
2 (87)
Range (%)
0–10
Range (%)
0–18
Studies not pooled. No events in one
trial and very wide CIs in other trial.
Insufficient
Withdrawals due to adverse effects
2 (87)
Range (%)
0–5
Range (%)
0–14
Studies not pooled. No events in one
trial and very wide CIs in other trial.
Insufficient
Participants with 1 adverse effect
Not reported
Insufficient
CI = confidence intervals; I-PSS = International Prostate Symptom Score; QoL = quality of life; RR = risk ratio; WMD = weighted mean difference.
Downgraded based on the following:
a
Risk of bias (moderate).
b
Imprecision.
c
Unknown consistency or inconsistency.
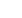
Table 6 – Evidence overview of tadalafil 5 mg versus tamsulosin 0.2–0.4 mg monotherapy
Outcome
No. of trials
(evaluated)
Intervention,
% (
n
/
N
) or mean
Control,
% (
n
/
N
) or mean
Results and magnitude
of effect (95% CI)
Strength of
evidence
Responders
Not reported
Insufficient
I-PSS score, mean change from baseline
3 (742)
–5.6 points
–5.9 points
Similar between groups:
WMD –0.07 (–2.12 to 2.23)
Moderat
e aI-PSS QoL, mean change from baseline
3 (742)
–1.1 points
–1.1 points
Similar between groups:
WMD –0.01 (–0.75 to 0.73)
Lo
w a , cOverall withdrawals
3 (742)
10 (36/373)
8 (28/369)
Similar between groups:
RR 1.35 (0.30–6.05)
Lo
w a , bWithdrawals due to adverse effects
3 (742)
3 (11/373)
1 (4/369)
Greater with tadalafil:
RR 2.68 (1.09–6.60)
Moderat
e aParticipants with 1 adverse effect
3 (742)
25 (94/373)
24 (90/369)
Similar between groups:
RR 0.99 (0.38–2.56)
Lo
w a , bCI = confidence intervals; I-PSS = International Prostate Symptom Score; QoL = quality of life; RR = risk ratio; WMD = weighted mean difference.
Downgraded based on the following:
a
Risk of bias (moderate).
b
Imprecision.
c
Unknown consistency or inconsistency.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 1 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 5 7 0 – 5 8 1
576